Epithelial tissue is a layer of cells that covers the body’s surface. It forms the lining of all body cavities and organs, and it protects against infection and injury. Epithelial tissue also regulates the movement of fluids and nutrients across its surface.
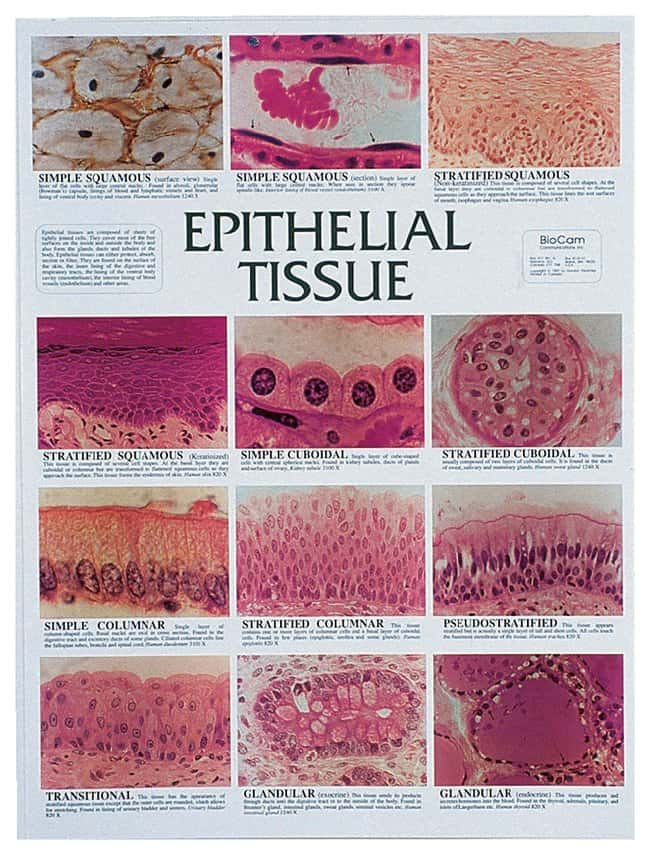
There are three main types of epithelial tissue: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal.
Epithelial tissue is one of the four major tissue types in the human body. It is made up of cells that line the internal and external surfaces of the body, including the skin. Epithelial tissue provides a barrier between the inside and outside of the body and helps to protect against infection.
This type of tissue also helps to regulate fluid balance and absorb nutrients from food.

Credit: www.youtube.com
What are the 4 Types of Epithelial Tissue?
There are four types of epithelial tissue in the human body: squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and transitional. Each type is distinguished by its shape and function.
Squamous epithelial cells are flattened and scale-like in appearance.
They form the lining of blood vessels and cavities where there is little movement or stress, such as the lining of the respiratory tract. Cuboidal epithelial cells are cube-shaped and typically line ducts and tubules where there is moderate movement or stress, such as the kidney tubules. Columnar epithelial cells are tall and slender, arranged in rows like columns.
They line areas where there is significant movement or stress, such as the intestine. Transitional epithelial cells have a variable shape that can be either flat or rounded depending on the level of movement or stress in the area they line. Examples include the bladder and ureters which must expand when filled with urine but return to their normal shape when empty.
What are the 4 Main Functions of Epithelial Tissue?
Epithelial tissue is one of the four main types of tissues in the body. It is made up of cells that line the surfaces of organs and body cavities, and it plays an important role in protecting the body from infection and injury.
The four main functions of epithelial tissue are:
1. Protection: Epithelial tissue forms a barrier between the internal organs and the external environment, preventing harmful substances from entering the body and protecting the organs from mechanical damage.
2. Absorption: Epithelial tissue lining the gut absorbs nutrients from food and water.
3. Secretion: Some epithelial cells secrete mucus, sweat, or other substances that lubricate or protect surfaces.
Other epithelial cells secrete hormones that regulate various body processes.
What is the Function of a Epithelial Tissue?
Epithelial tissue is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity. The main function of epithelial tissue is to protect the body from infection, injury, and dehydration. Epithelial tissues also absorb nutrients, produce hormones, and remove wastes.
There are three main types of epithelial tissue: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal.
Squamous epithelium is thin and flat with irregularly shaped cells. It forms the lining of blood vessels, air sacs in the lungs, and the outer layer of skin.
Columnar epithelium is taller than it is wide with elongated cells arranged in rows. Columnar epithelium lines the stomach and small intestine where absorption occurs. Cuboidal epithelium has cube-shaped cells arranged in rows.
It forms kidney tubules and ducts in glands.
What Organs are Epithelial Tissue?
Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that is made up of cells that are closely packed together. This tissue forms the outer layer of the body and covers all surfaces that come in contact with the outside world, such as the skin, mucous membranes, and the linings of blood vessels and organs.
There are three main types of epithelial cells: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal.
Squamous epithelial cells are flat and scale-like in appearance. Columnar epithelial cells are taller than they are wide and have a cylindrical shape. Cuboidal epithelial cells are cube-shaped.
Epithelial tissue can be found in many different parts of the body, including:
-The outer layer of the skin
-The lining of the mouth, nose, lungs, and other organs
-The linings of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels
Tissues, Part 2 – Epithelial Tissue: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #3
Epithelial Tissue Function
Epithelial tissue is one of the four types of tissues that make up the human body. It is made up of cells that are closely packed together and held in place by special junctions. The main function of epithelial tissue is to act as a barrier between different areas of the body or between the body and the outside world.
Epithelial tissue covers all surfaces of the body, both internal and external. It forms the lining of cavities such as the digestive tract, respiratory tract, urinary tract, and blood vessels. It also makes up glands such as sweat glands and oil glands.
The cells of epithelial tissue are tightly joined together at their edges by special structures called junctions. There are three types of junctions: tight junctions, adherens junctions, and desmosomes. Tight junctions form a seal between adjacent cells, preventing anything from passing through the spaces between them.
Adherens junctions hold cells together using proteins that attach to molecules on the surface of adjacent cells. Desmosomes help to anchor cells to each other by attaching intermediate filaments to plaque proteins in adjacent cell membranes.
The type of junction present determines how permeable the epithelium is; for example, tight junctions make an epithelium impermeable while adherens junctions allow some passage through gaps between cells (1).
The type of cell junction present also influences cell communication; for example gap junction proteins allow direct communication between adjacentcells while desmosome proteins mediate indirect communication (2).
Conclusion
Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that covers the surface of the body and line internal cavities. It consists of closely packed cells that are held together by cell junctions. The junctions between epithelial cells help to keep the tissue from drying out and prevent bacteria and other microorganisms from getting in.
Epithelial tissue is also found in glands, where it helps to produce and secrete substances such as hormones and enzymes.