There are many different types of connective tissue disease, and the symptoms can vary depending on the individual. Connective tissue is the material that connects and supports all other tissues in the body, so when it is diseased, it can cause a wide range of problems. The most common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, muscle pain, and Raynaud’s phenomenon (a condition where the blood vessels in the hands and feet constrict in response to cold or stress).
Some people may also experience skin problems such as rashes or scleroderma (a condition where the skin becomes thick and hard). In severe cases, connective tissue disease can lead to organ damage or failure. Treatment for connective tissue disease typically focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing further damage to the body.
There are many different types of connective tissue disease, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment options. Some common connective tissue diseases include lupus, scleroderma, and dermatomyositis. While there is no cure for any type of connective tissue disease, early diagnosis and treatment is essential in managing the symptoms and preventing further damage to the body.
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. The most common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and fever. Lupus can also cause kidney problems, high blood pressure, hair loss, and anemia.
There is no cure for lupus but treatments are available to help manage the symptoms.
Scleroderma is a chronic condition that causes hardening and tightening of the skin. It can also affect the internal organs such as the heart, lungs, and kidneys.
Symptoms vary from person to person but can include Raynaud’s phenomenon (a condition that causes your fingers or toes to turn white or blue when exposed to cold temperatures), joint pain, gastrointestinal problems, and difficulty swallowing. There is no cure for scleroderma but treatments are available to help manage the symptoms and prevent organ damage.
Dermatomyositis is a rare inflammatory muscle disease that primarily affects children aged 5-15 years old.Symptoms include muscle weakness (often starting with difficulty climbing stairs or getting up from a chair), rash on eyelids or cheeks (heliotrope rash), photosensitivity (increased sensitivity to sunlight), weight loss, fatigue ,and fever .

Credit: www.stleonardsphysio.com.au
What are the Symptoms of Connective Tissue Disease?
There are many different types of connective tissue disease, each with its own set of symptoms. However, there are some general symptoms that are common to most types of connective tissue disease. These include:
-Joint pain and stiffness: This is often the first symptom of connective tissue disease, and can be particularly severe in the morning or after periods of inactivity. The joints may also swell and feel warm to the touch.
-Muscle weakness and fatigue: Connective tissue disease can cause muscles to weaken and tire easily.
People with the condition may also have difficulty climbing stairs or carrying heavy objects.
-Skin rashes: Many types of connective tissue disease cause a distinctive skin rash, which may be itchy or painful. The rash may come and go, or it may be permanent.
-Sensitivity to cold: People with connective tissue disease often find that they are sensitive to cold temperatures. They may feel chilly even when others are comfortable, and they may need to layer their clothing to stay warm.
-Dry eyes and mouth: Dryness of the eyes and mouth is another common symptom of connective tissue disease.
This can lead to problems with vision and chewing/swallowing food.
What are Common Connective Tissue Disorders?
There are many different types of connective tissue disorders, but some of the more common ones include:
-Osteoporosis: This is a condition in which the bones become weak and fragile due to a loss of bone mass. It is most common in older adults, but can also affect younger people.
-Rheumatoid arthritis: This is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects the joints and other tissues. It can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints.
-Lupus: This is a chronic autoimmune disorder that can affect various parts of the body including the skin, joints, kidneys, and brain.
It can cause fatigue, joint pain, rash, and fever.
What is the Treatment for Connective Tissue Disease?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the treatment for connective tissue disease will vary depending on the specific condition diagnosed. However, some common treatments for connective tissue diseases may include physical or occupational therapy, medications (such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants), and surgery. In some cases, patients may also need to make lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers that can worsen symptoms or learning ways to cope with pain.
How Long Can You Live With Connective Tissue Disease?
There is no one answer to this question as the length of time someone can live with connective tissue disease varies depending on the individual and the severity of their condition. However, it is possible for people with connective tissue disease to have a normal life expectancy if their condition is managed effectively. In severe cases, however, connective tissue disease can lead to organ damage and failure, which can be fatal.
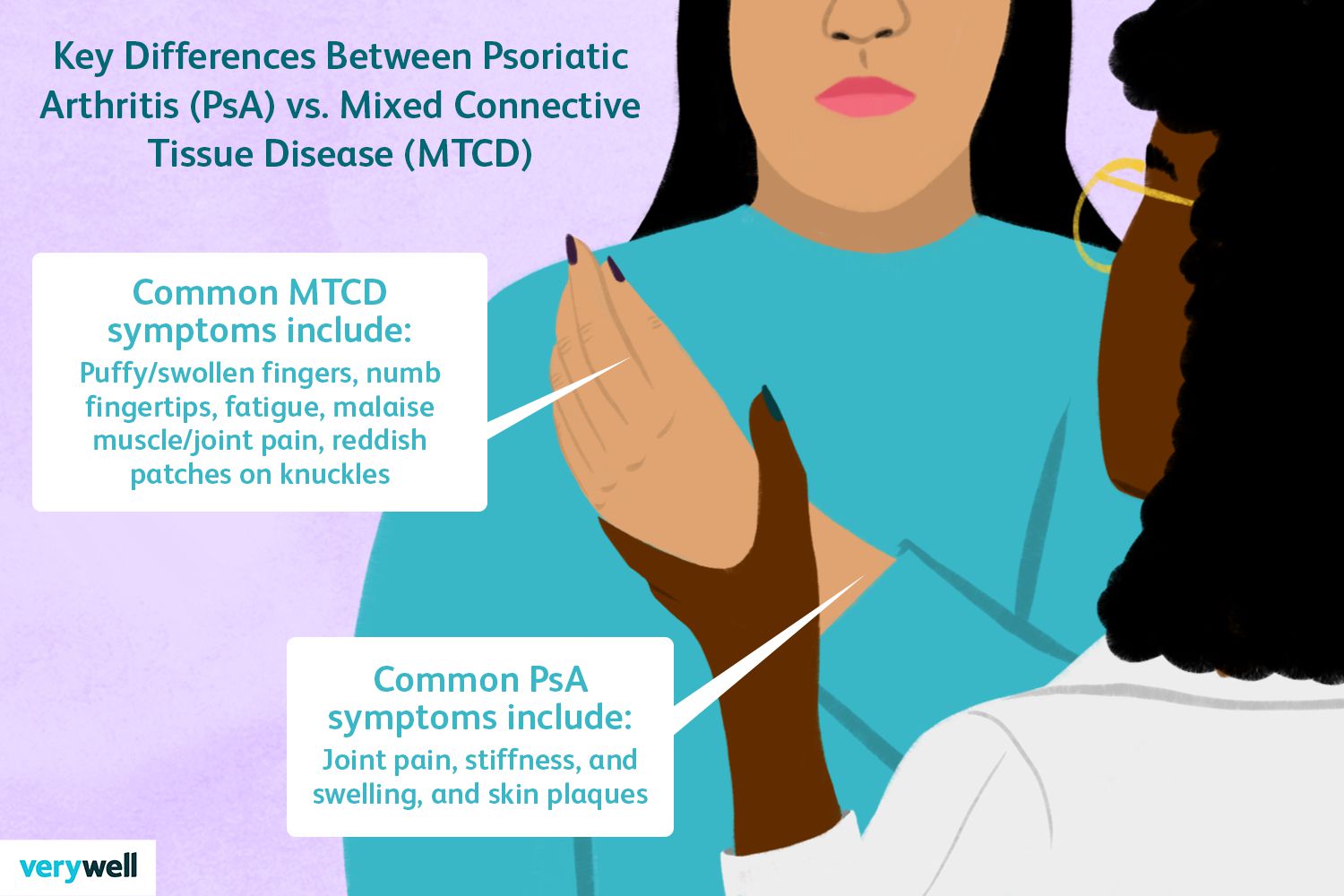
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease mnemonic
Connective Tissue Disease Symptoms
What is Connective Tissue Disease?
Connective tissue disease (CTD) refers to a group of disorders that affect the parts of the body that connect tissues and organs together. These diseases can cause problems with any part of the body, including the skin, joints, and internal organs.
There are many different types of CTDs, and they can vary in how severe they are. Some people with CTD may only have mild symptoms, while others may be more severely affected. Symptoms also tend to differ from person to person depending on which type of CTD they have.
The most common symptom of CTD is joint pain or stiffness. This is often worse in the morning or after periods of rest. Other common symptoms include: fatigue, muscle aches and pains, Raynaud’s phenomenon (a condition where blood flow to the fingers and toes is reduced), skin rashes, mouth sores, dry eyes or mouth, and difficulty swallowing.
Some people with CTD also experience problems with their internal organs. This can lead to difficulties such as shortness of breath, heartburn, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation. In some cases, these problems can be serious enough to require hospitalization.
Diagnosis & Treatment
There is no single test that can diagnose CTD. Instead, diagnosis usually involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination findings ,and laboratory testing .
Your doctor may also refer you to a rheumatologist (a doctor who specializes in treating arthritis and other inflammatory conditions) for further evaluation . No specific cure exists for most forms of CTD , but treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications . This may involve medication , lifestyle changes ,and surgery in some cases .
Conclusion
Connective tissue disease is an autoimmune disorder that occurs when the body’s immune system attacks healthy connective tissue. Connective tissue is found in all parts of the body, including the skin, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels. When connective tissue is damaged, it can cause a wide range of symptoms, depending on which parts of the body are affected.
Common symptoms include joint pain and stiffness, muscle weakness, fatigue, skin rashes, and problems with internal organs. There is no cure for connective tissue disease, but treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.